Financial Instruments – Introduction
Markets have diverse financial instruments catering to unique requirements of traders and investors across the globe. These include – stocks, commodities, cryptos, Forex etc.
Understanding these financial instruments is important as to how they fundamentally differ from each other. These are traded for different times, have different volatility, risk profiles and consequently the returns.
Spot market
A spot market, also known as a cash or physical market, is a financial market where various financial instruments, commodities, or assets are traded for immediate delivery and settlement. Transactions in the spot market involve the direct exchange of goods, securities, or cash.
While trading is possible in spot market, it is less popular for the following reasons:
- Lack of Leverage
- Absence of Risk Management Tools
- High Taxation and Transaction Costs
- Stocks

Stock market is a place where shares are bought and sold of publicly traded companies eg Apple, Microsoft, Tesla etc.
Stocks are generally bought for a long period of time for wealth creation aka investing and holding shares of a company means you own a portion of that company.
Stocks can also be held for short term (trading) – Intraday and Swing trading.
In intraday, shares are bought/sold on the same day whereas swing trading involves holding positions from days to weeks.
Traders usually avoid trading stocks as stocks are not leveraged instruments which reduces the expected returns.
Stocks should primarily be held for investment purposes only from months to years targeting capital appreciation and dividends.
- Cryptocurrency

Cryptocurrency market is a digital marketplace where cryptos like bitcoin and ethereum are traded. Cryptocurrency is relatively new among financial instruments class built on the latest technology, not backed by any physical asset.
Bitcoin acts as an index for cryptocurrency which also acts as sentiment crypto for all other cryptocurrencies i.e, if Bitcoin is bullish, other coins tend to follow it.
Cryptocurrency market is open 24×7 and accessible through various exchanges across all countries.
This asset class is highly volatile and risky and hence, also the most rewarding.
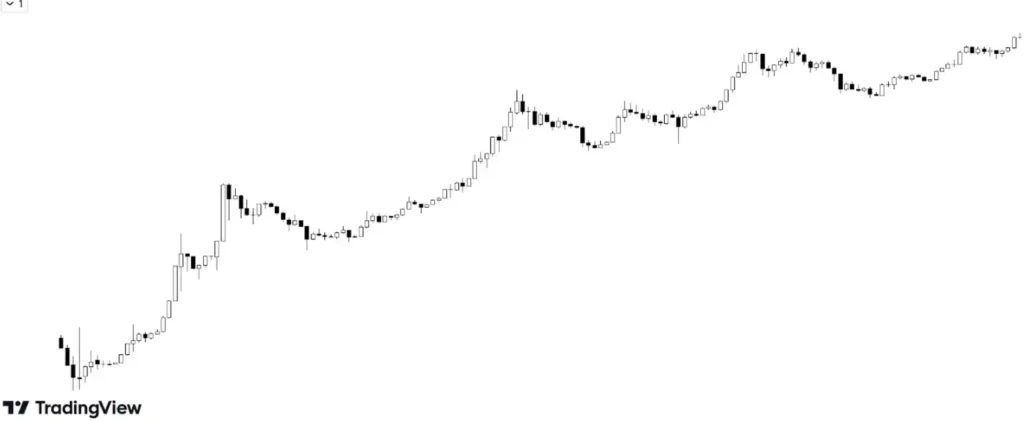
The above chart shows the appreciation of Bitcoin from 2012 to 2025. As cryptocurrency is being accepted worldwide, bitcoin is reaching new heights every year.
Cryptocurrency, in its initial phase, was seen only as a speculative instrument but as new technologies are being built on blockchain technology, traders are now also looking for investment opportunities.
- Commodities

In the commodity market, commodities like gold, oil, agricultural products etc are traded. Unlike stocks, commodities represent physical asset rather than ownership in a company,
There are generally two types of participants here, speculators (traders) and hedgers. Traders aim to profit from price volatility and provide liquidity in return,
Hedgers such as farmers and manufacturers, take positions in commodities to protect themselves from adverse price changes in future.
Although spot trading is possible, many traders prefer futures contracts or derivatives to avoid the complexities of physical delivery.
- Forex

Forex or foreign exchange market is the largest financial market in the world where currencies (USD, EUR,JPY etc) are traded.
Forex is commonly associated with speculation where traders speculate on the exchange rate movements between currency pairs eg USD/JPY.
It also serves the central banks of all the countries to hedge currencies and manage international payment.
Unlike spot commodity trading where physical delivery of the commodity occurs, in spot forex trading, there is no physical delivery of the currencies. The trade is purely a financial transaction, and the profit or loss is determined by the change in exchange rates.
Forex market is highly leveraged which increases both risk and reward.
Future and Options

Futures and Options (F&O) are derivative financial instruments which derive their value from an underlying asset such as stocks, indices, commodities, crypto or currencies.
F&O instruments are primarily used for:
- Hedging: Protecting portfolios from adverse price movements.
- Speculation: Profiting from price movements without owning the underlying asset.
- Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences in different markets.
Futures contracts are legally binding agreements to buy or sell a specific asset (stocks, cryptos) at a predetermined price (eg current price) on a specified future date.
Futures allow us to sell without owning an asset. Additionally, futures are leveraged instruments which allow us to carry big positions without having enough capital for it.
An option is a contract that gives the buyer, right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a pre-specified price (strike price) to the seller of call/put option.
If you buy a Call option, you will make profit when prices go up and if you sell, you will be in profit when prices go down whereas if you buy a Put option, you will make profit when prices go down and if you are a seller of a put option, you would make money if prices go up.
Key Takeaways
- Financial Instruments in markets include stocks, commodities, cryptos, and Forex, each with unique risks and returns.
- Spot markets offer immediate delivery but lack leverage and have high costs.
- Stocks are traded for long-term growth and dividends.
- Cryptocurrencies are volatile, 24/7, and risky but rewarding.
- Commodities trade physical assets, with speculators and hedgers.
- The Forex market trades currencies with high leverage.

